This is the first of a three-part series examining how companies are transforming their customer experience strategies through the use of technology.
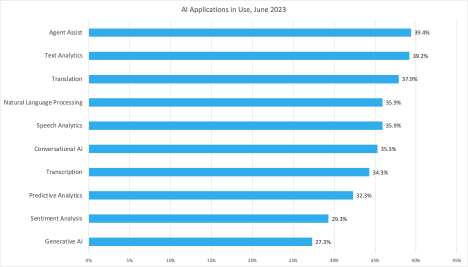
Artificial intelligence is fast becoming must-have technology for any successful customer engagement strategy. As our research shows, the documented improvements derived from the different types of AI (as shown in the following graph) are dramatically transforming how efficiently companies serve their customers.
Already, companies have AI-enabled 28 applications used for customer experience (CX), with plans to reach 72 applications by 2025, according to Metrigy’s Customer Experience Optimization 2023-24 global research study of 641 companies. AI is involved with resolving an average of 44.5% of customer interactions, which Metrigy projects will increase to 60.9% by 2025. Agent assist (software that leverages various types of AI to provide agents in-the-moment advice, information, and context to improve customer service or sales) is the most widely adopted use of AI so far (39.4%)—and with good reason. It reduces Average Handle Time (AHT) by 27.2%.
When used in customer engagement initiatives, the results are clear: AI is driving measurable success across several metrics, according to the study.
General use of AI in CX initiatives improves revenue by 19.6%, increases customer ratings by 20.5%, and boosts agent efficiency by 12.7%. Our research success group—those companies with higher-than-average success in multiple advanced CX technologies—shows even more impressive results, including 38% revenue increase, 45.8% customer ratings improvement, 5.6% operational cost decline, and 36% efficiency boost.
CX Transformation Takes Off
Figures like those are truly transformative. Indeed, in 2023 we have seen a huge jump in the number of companies transforming their customer experience: 82.7% of companies have completed, are in the process of completing, or planning a CX transformation project, up from only 53% in 2022.
By definition, CX transformation is the innovative application of new or existing technologies to improve the customer and/or agent experience to drive measurable business value.
AI is serving as a catalyst for change. Though some projects are foundational, such as platform integration or adding management tools, others involve new applications and channels. For example, 41.2% say their project involves adding or improving virtual assistants and chatbots, and 41.0% cite generative AI as their project. (More on generative AI in the next post in this series.)
AI’s Effect on Staffing
We are starting to see a compelling impact of AI on staffing. Metrigy estimates that those not using AI in their CX initiatives will need to hire 2.3 times the number of new agents in 2023 compared to those using AI! This is largely due to the efficiency gains delivered by AI, as discussed above.
Translating that into dollars, it’s about $4.3 million a year in savings—for compensation alone. It doesn’t even include equipment, application licenses, office space, etc. These figures vary by company size, but given companies will spend, on average, about $500,000 in 2023 on AI, the payback is enormous. (Note: this average refers to all costs whether implementation or ongoing licensing.)
AI apps are projected to have the most impact on staffing, in terms of cost savings, include generative AI, virtual assistants, speech analytics, sentiment analysis, and agent assist.
It’s important to note, we do not see AI causing layoffs at this time. In fact, 46.5% of companies plan to increase the number of contact center licenses in use by 2024, and only 6.6% plan to decrease the number of licenses. So, companies are continuing to hire in the contact center, but not at the high numbers they once did.
The figures for staffing are encouraging otherwise, as well. Contact center turnover rates have dropped to 21.8%, after an increase to 30.5% during the pandemic. And most (58.3%) contact centers are now fully staffed. Companies using agent assist are 20% more likely to be fully staffed than those who do not.
AI’s Effect on Sales
Contact center and sales leaders are using AI to improve revenue. AI can monitor trends, keywords, levels of engagement, sales team interactions, and macro-economic factors. And all of this information provides insight for managers to be more effective.
For example, if managers can more accurately predict revenue or shortfalls for the quarter, they can take action to mitigate. Natural Language Processing and sentiment analysis can evaluate conversations to identify opportunities that have the most likelihood of closing—shifting agents or sales reps to focus on those deals. AI also can identify differences in top performers and deliver personalized sales training to those who are not top performers.
Sales performance is becoming more vital in the contact center, as 54.3% of companies have assigned sales quotas to customer service representatives. This is a way for companies to increase revenue overall and became particularly popular during the pandemic. It also offers a way to pay agents more through commission plans.
Agent assist, again, emerges as the top technology, in this case for helping to close sales: 42% of companies are using it in that manner, followed by virtual assistants (39.6%), personalized online sales training (38.9%) and analytics (34.5%).
Job Shifting Will Become the Norm
AI clearly has and will continue to have an impact on jobs. Yes, it will cause some people to lose jobs, as any technology advancement does. But it also will help to create jobs, automate mundane tasks that people prefer not to do, and make existing jobs more efficient.
AI will create more jobs for data science and data analytics, so business and CX leaders know what actions to take based on the mounds of new data being gathered. It also creates jobs for content managers, whose role is to ensure company knowledge base data is accurate, creative, and multimedia.
Nearly three-quarters of companies say AI helps them to augment staff shortages by making existing agents more productive (52.1%), handling inquiries in place of agents (49.5%), or offloading mundane tasks, such as the value of transcription replacing the time sink of after-call notes (47.9%). Because of these productivity boosts, some agents will lose their jobs to AI, but so far, we are not seeing this in large numbers. However, as stated, we do see a reduction in the number of new hires.
Moving forward, we expect to see companies increase their utilization of AI for their CX initiatives, with generative AI being a driver and accelerator of CX transformations. In the next post of this three-part series, I’ll cover Metrigy’s findings on generative AI specifically.